10 Tips on How to Control Diabetes Without Medication
Here, you are going to discover 10 tips on how to control diabetes without medication. Now, if you are in a hurry, then click here to go straight to the ten tips list.
However, I believe that it is always best to understand the basic underlying issues of a problem to fully appreciate just how effective any given solution can be.
So, if you have the time, why not spend a few minutes getting to grips with what diabetes is, its potentially life-threatening risks, and how it is treated, before moving on to understanding how to help control it without medication.
Once again, click here:- How to Control Diabetes Without Medication if you are short on time, otherwise join me on an intriguing journey through the basics first...
Famous People With Diabetes
The Role of Glucose and Insulin in the Body
To get a real understanding of diabetes you first need to understand about the roles of glucose and insulin in the body...
Glucose
The cells and organs in the human body need energy to survive and carry out the myriad of processes they were 'designed' for. All energy needs fuel of some sort and in the case of the body's cells that fuel is glucose.
Glucose is a simple sugar that is produced in the small intestine -- from the sugar and starch (complex carbohydrates) that we consume -- where it is taken up in the blood and circulated around the body.
Glucose molecules are transferred out of the bloodstream into the cells through microscopic blood vessels called capillaries. However, on its own, this isn't sufficient to provide the energy needed...
Oxygen -- via red blood cells -- is also transferred from the capillaries into the cells. This vital component helps to 'burn-off' the glucose and so release the energy that the cells use to survive and function.
Insulin
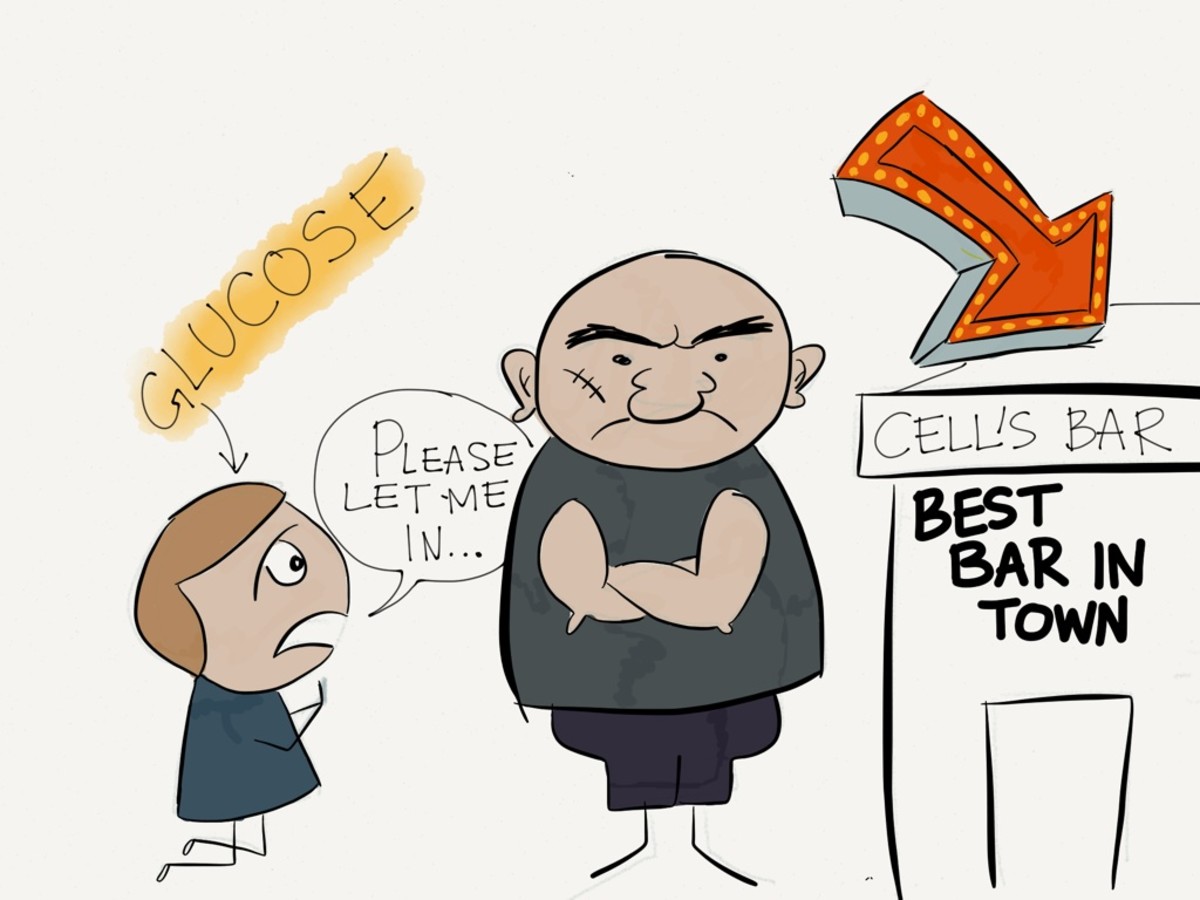
Where does insulin come into play? Well, glucose cannot penetrate the protective cell wall on its own and insulin is the key that 'unlocks' this barrier.
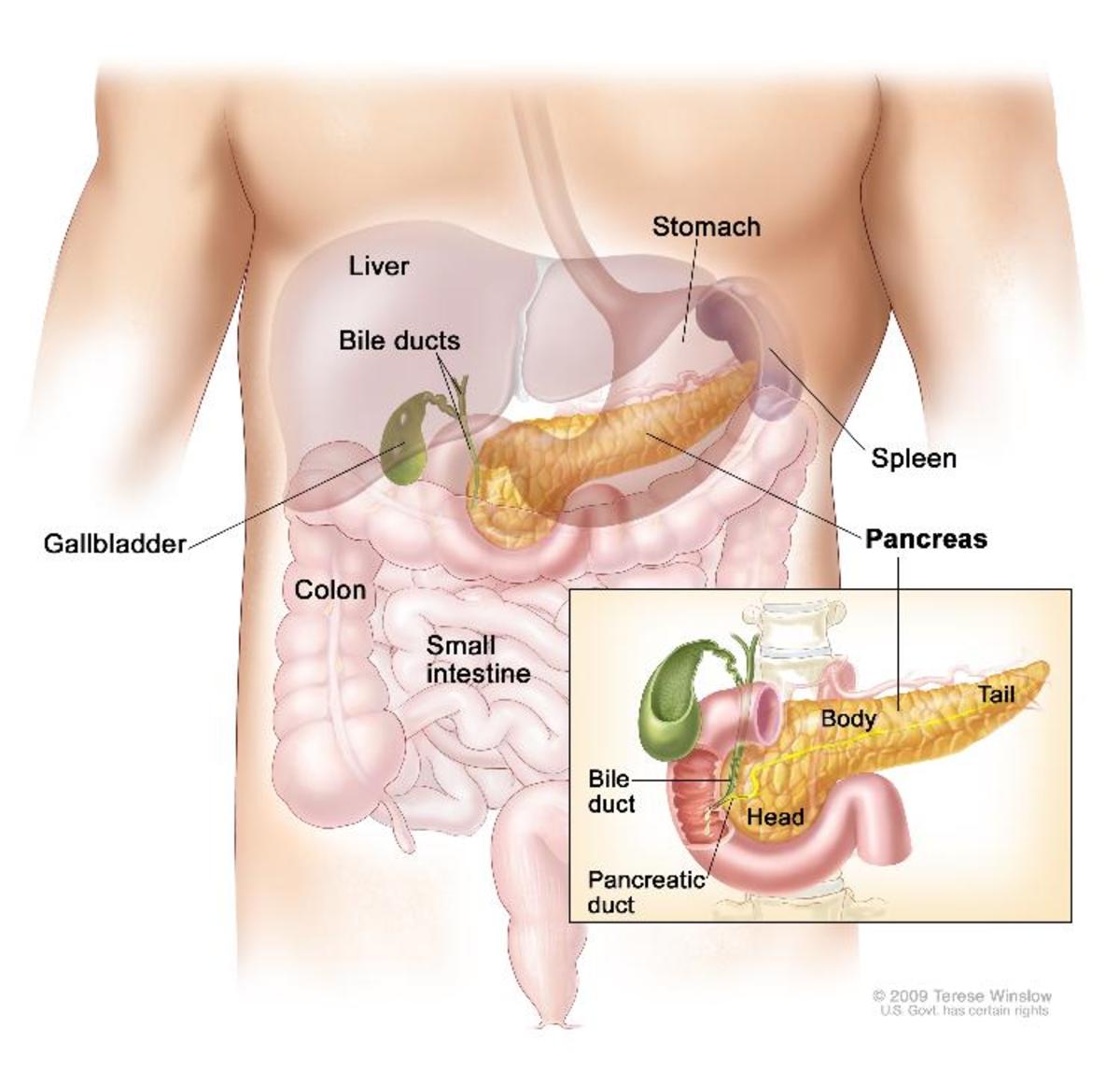
So that when the pancreas detects rising glucose levels in the blood it injects insulin -- a hormone -- into the blood to help the glucose molecules pass through the protective walls into the cells.
In this way insulin helps regulate and maintain the body's blood-glucose levels within a normal range so that the body always has sufficient glucose to function correctly.
However, there is a further process to consider, and that is how excess glucose in the blood is stored...
Glycogen
The body stores excess glucose in the liver and muscles to provide its energy needs in case of emergency, e.g. during starvation, or, when the body needs energy fast , e.g. for running or exercising.
But glucose, being a very small molecule, cannot be stored in body tissue: it is a bit like trying to store water in muslin. So it is converted into 'glycogen,' a much bigger, more complex sugar than glucose; a single glycogen molecule consisting of as many as 30,000 glucose molecules.
When glucose is required by the body in an emergency, in the case of the liver, the glycogen is then converted back into glucose and introduced into the bloodstream where it can be taken up by the body's cells.
Muscles, on the other hand, lack the enzyme needed to pass glucose into the blood so muscle reserves of glycogen are used as the fuel source for the local area and not the rest of the body.
The important thing to understand is that all the processes above are dependent on a normally functioning insulin system, which leads us nicely into looking at the diabetes condition itself...
What is Diabetes?
According to the American Diabetes Association and based on data from the 2011 National Diabetes Fact Sheet, nearly 26 million Americans have diabetes of whom 7 million are undiagnosed, i.e. do not know they have it.
It is a similar story in the UK where, according to Diabetes UK, there are some 3 million sufferers, with around 850,000 of them being undiagnosed.
Diabetes -- clinical title diabetes mellitus -- is a condition whereby insufficient insulin (or none at all) is produced by the body. This leads to high glucose levels in the blood because not enough is being taken up by the body's cells.
There are two types of diabetes; Type 1 and Type 2 and according to eMedicineHealth 10% of diabetes sufferers have Type 1 and 90% have Type 2.
Type 1 diabetes is where the pancreas produces no, or not enough, insulin for correct blood glucose regulation.
Because glucose needs insulin to help it penetrate a cell's protective membrane and so enter the cell, this situation not only starves the body's cells of their fuel (glucose) but also causes harm and damage to organs and body tissue exposed to excess glucose.
Type 1 is more prevalent in childhood and adolescence although it can appear in adulthood, especially where the pancreas has been compromised in some way, e.g. through too much alcohol consumption or disease.
Patients with type 1 diabetes require insulin on a daily basis in order to stay alive.
Type 2 diabetes is the condition where the pancreas does produce sufficient insulin but the body is resistant to the insulin and so glucose levels in the blood rise as insufficient is being taken up by the body's cells.
The pancreas's solution for this is to inject even more insulin into the blood which the body just cannot cope with. This leads to even higher blood-sugar levels which can trigger several complications if not treated properly.
Type 2 is more generally found in the adult population, particularly the over-40's, but can be present in younger people.
It is usually controlled using diet, exercise, weight-loss and sometimes oral drugs where appropriate. If this strategy fails then patients will need to control their blood-sugar levels through insulin therapy.
Natural Products to Help Control Diabetes
Risks and Complications
Some of the commonly known complications with diabetes are:-
- strokes
- heart attacks
- blindness
- circulation issues
- kidney failure
But there is also some disturbing statistics surrounding the increased risk of death in patients with diabetes...
Research published in the New England Journal of Medicine, comparing patients with diabetes against people without diabetes and summarized in WebMD, shows that having diabetes...
- doubles the risk of death from a heart attack or stroke
- triples the risk of death by kidney disease
- doubles the risk of death from liver cancer (more modestly for other cancers)
- doubles the risk of death through infectious disease
So it is clear that diabetes is a serious condition that needs to be diagnosed early and treated and managed closely.
What type of Diabetes do you have?
Blood Glucose Monitors
How to Control Diabetes Without Medication
The following 10 tips will help you manage your condition more effectively...
1. Monitor Your Glucose Levels Regularly
You cannot manage what you cannot measure, so monitor your blood sugar levels regularly using a home monitor.
Your doctor will advise on your target range and when and how often to measure your blood sugar depending on your particular case.
Keep an ongoing record and work closely with your doctor to help manage your glucose levels in the most effective manner.
2. Eat Your Meals at Regular Times
Try to eat your meals more or less at the same times every day, certainly within an hour of the appointed times.
Not only will this help you control your blood sugar more effectively, it will also make it easier for you to monitor your blood glucose levels.
And never, ever skip meals.
3. Eat a Healthy Balanced Diet
Consult with your doctor and / or dietitian about the best meal plan for your particular case. The key here is a healthy 'balanced' diet.
Try to ensure you have a wide range of healthy foods that will give you the essential nutrients, vitamins, minerals, etc. your body needs.
Balance your protein, carbohydrates and fats.
Eat plenty of fibre-rich fruit, vegetables, nuts, legumes, and wheat bran etc.
Don't over-eat: you don't need to fill every available space on your plate.
4. Always Read Food Labelling
Since you must track what you eat it's really important to inspect all food labels.
Understand serving size and associated carbohydrate, fat (good and bad), and calorific content is an essential part of controlling your diabetes.
5. Exercise Daily
Daily exercise is just so important. But don't give yourself impossible targets to hit at first.
If you haven't exercised for some time talk to your doctor first about a low key approach and gradually work up to at least 30 minutes per day, an hour if possible.
Make it something you enjoy rather than a chore that's hard to maintain. Swimming, cycling, walking, dancing, etc.
6. Optimize Your Weight
Exercising, combined with a healthy balanced diet, will undoubtedly help you to shed those pounds, but you need to stick with it and not be put off.
Talk to your doctor about your ideal healthy weight. They will take the appropriate measurements to ascertain your ideal weight and set yourself that as your target.
But do not go for 'fad' diets. These can cause havoc with your condition by causing uncontrolled rapid changes in blood sugar. And you end up putting on the pounds again anyway.
7. Reduce Stress
Stress can negatively affect diabetes directly through stress hormones which can alter your blood sugar levels.
Stress can also affect diabetes indirectly, because it can cause a patient to not take care of themselves appropriately for their condition.
Do all that you can to reduce the stress in your life. Things such as daily exercise, breathing exercises, yoga, relaxation techniques, better time management, and so on.
8. Avoid or Reduce Alcohol Consumption
Whilst low levels of alcohol can increase blood sugar, excess alcohol consumption can actually lower blood sugar to sometimes dangerous levels.
Alcohol can stimulate your appetite resulting in you overeating and so interfering with effective blood glucose control.
And alcohol can adversely affect insulin and oral medications for diabetes.
It's best to avoid alcohol altogether, but, at the very least, limit yourself to 2 alcoholic drinks per day. One alcoholic drink in this context is 1 x 5 ounce glass of wine, 1 x 12 ounce glass of beer, or 1 x 1/2 ounce shot of liquor.
If you must take alcohol then drink it slowly and with food where possible. And adding water or drinking water alongside is a good idea too.
9. Examine Your Feet Regularly
Diabetics can often suffer from a variety of foot problems mainly due to poor blood flow and nerve damage brought on by the diabetes.
Check your feet on a daily basis, using a mirror to examine the parts that are hard to see.
Be careful not to damage or cut the skin as these are often difficult to heal in diabetics. So do not walk in bare feet (even in the house), sandals, flip-flops etc. Wear well-fitting shoes
As a diabetic the care of your feet is very important, and this includes the nails, therefore regular trips to a chiropodist could be beneficial.
Regular visits to a podiatrist are also called for even if you cannot see anything wrong.
Wash your feet daily in warm water, but do not let them soak. Just wash them with mild soap, rinse, then dry gently, taking care to ensure you dry between the toes.
If you have sores or cuts or abrasions that do not heal then visit your doctor for advice.
10. Keep In Touch With Your Doctor
Regular checkups are an essential part of an effective diabetes control plan.
At each appointment, your doctor should check your weight, blood pressure and feet to look for any significant changes that need addressing.
Your doctor would also wish to know how effectively you are managing your diabetes. They will normally do this through the A1c blood test which will give your average blood sugar level over a period of two to three months.
Note: The above tips on how to control diabetes without medication are relevant to both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes since, although their origins and treatment regimens may be different, their complications are much the same and both require strict dietary and lifestyle changes to be made. But do not cease any diabetes medications whilst implementing these natural ways of controlling diabetes.
References for How to Control Diabetes Without Medication
- http://diabetes.webmd.com/drinking-alcohol
- http://health.howstuffworks.com/diseases-conditions/diabetes/diabetes1.htm
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycogen
- http://orthomolecular.org/nutrients/glycogen.html
- http://www.diabetes.org/living-with-diabetes/complications/foot-complications/
- http://diabetes.niddk.nih.gov/dm/pubs/overview/
- http://www.mentalfloss.com/difference/type-1-vs-type-2-diabetes/
- http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/diabetes-diet/DA00027
- http://www.helpguide.org/life/healthy_diet_diabetes.htm
Disclaimer
The content of this Hub is for informational purposes only. It is not meant to be a substitute for proper medical diagnosis, treatment or advice, and you should not assume that it is. Always consult your health-care provider / physician / doctor before taking any medications, natural remedies, supplements, or making any major changes to your diet.